There have been arguments both in favor and against ever since.
His team of researchers provided their test subjects with photos of faces showing different emotional responses.
From this study, the six basic emotions were proposed.

God & Man
However, some peoplebelievethere are eight basic emotions.
These core emotions are joy, sadness, anger, fear, trust, distrust, surprise, anticipation.
Happiness is characterized by a facial expression that causes someone to raise the corners of their mouth upwards.

Surprisingly, however, disgust is one of the 6 emotions that decreases heart rate.
Facial Expression/Emotion: Fear
Fear is an emotion that is often associated with a threatening or dangerous stimuli.
Facial Expression/Emotion: Surprise
Surprise is an emotion that is often associated with a brief state of being.
This brief state of being is invoked by an unexpected, relevant event.
However, surprise isnt always a traumatic emotional experience.
We are easily able to hide these emotions from those around us, but they still exist.

Or do we need to dig deeper into the basic human emotions to understand them?
Plutchiks Wheel of Emotions is similar to a colour wheel.
Plutchiks eight primary emotions areJoy,Trust,Fear,Surprise,Sadness,Anticipation,Anger, andDisgust.

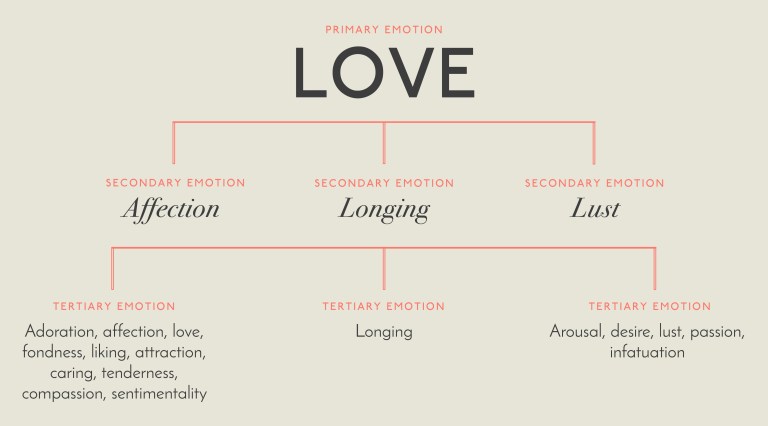
Parrotts Tree-Structured Theory
Another theory that has gained notoriety isParrotts tree-structured approachto human emotions and their layers.
Some of these emotions were not categorized by human expression, but rather, emotional states.
Anticipation:an emotion involving pleasure, excitement, or anxiety in considering an expected event.

Lappel du vide:A French term referring to the call of the void.
It describes the appeal of self-sabotage.
Awumbuk:the empty feeling we experience when a person who has visited us recently leaves.

Bafflement: to be confused, bewildered, or perplexed.
Basorexia: a strong craving or hunger for kissing.
Befuddlement: to confuse, as with glib statements or arguments.
Bewilderment: a feeling of being perplexed and confused.
Boredom: a specific mental state that people find unpleasanta lack of stimulation that leaves them craving relief.
Brabant: when you push someones buttons just to see if you could.
Broodiness: unhappy,or moody.
It also refers being in a state of serenity, tranquillity, or peace.
Carefree: free from anxiety or responsibility.
Cheerfulness: the quality or state of being noticeably happy and optimistic.
Claustrophobia: the fear of being enclosed in a small space or room and unable to escape.
Collywobbles: intense anxiety or nervousness, especially with stomach queasiness.
Comfort: a sense of physical orpsychologicalease, often characterized as a lack of hardship.
Compassion: sympathetic pity and concern for the sufferings or misfortunes of others.
Comparison: the feeling of joy one has experiencing anothers joy.
Contempt: a mixture of disgust and anger.
Desire: a sense of longing or hoping for a person, object, or outcome.
Despair: the complete loss or absence of hope.
Disappointment: the feeling of dissatisfaction that follows the failure of expectations or hopes to manifest.
Disgruntlement: to make ill-humored or discontented.
Discrete emotion theory: a theory that specific core emotions are biologically determined.
Disgust: an emotional response of revulsion to something considered offensive, distasteful, or unpleasant.
Dismay: consternation and distress, typically that brought on by something unexpected.
Dolce far niente:pleasant relaxation in carefree idleness.
Dread: anticipate with great apprehension or fear.
Exasperation: a feeling of intense irritation or annoyance.
Excitement: a feeling of great enthusiasm and eagerness.
Fear: a feeling induced by perceived danger or threat.
Frustration: a common emotional response to opposition.
Gezelligheid: coziness, fun.
It is often used to describe a social and relaxed situation.
Gladsomeness: giving or showing joy : cheerful.
Glee: great delight.
Gratitude: the quality of being thankful; readiness to show appreciation for and to return kindness.
Greg jai: of Thai origin; to be considerate, unobtrusive, not causing another person problems.
Hatred: a deep and extreme emotional dislike, especially invoking feelings of anger or resentment.
Hiraeth: a Welsh word which means nostalgia, or, more commonly, homesickness.
Hopefulness: inspiring hope; promising.
Homesickness: the distress triggered by being away from home.
Humbleness: having or showing a modest or low estimate of ones own importance.
Humiliation: the action of humiliating someone or the state of being humiliated.
Hwyl: a stirring feeling of emotional motivation and energy.
Ijirashi: a feeling that you get when you see someone who is praiseworthy.
Ilinx: the strange excitement of wanton destruction.
Impatience: the tendency to be impatient; irritability or restlessness.
Indignation: anger or annoyance provoked by what is perceived as unfair treatment.
Inhabitiveness: a propensity to remain permanently in the same place or residence.
Irritation: the state of feeling annoyed, impatient, or angry.
Kaukokaipuu: The feeling of unshakable longing for a place youve never been to.
Litost: a nearly untranslatable Czech word, a state of feeling miserable and humiliated.
Loneliness: a complex and usually unpleasant emotional response to isolation.
Matutolypea: the state of being in a bad mood or annoyed-especially in the morning.
Mono no aware: a Japanese term for the awareness of impermanence or transience of things.
Morbid curiosity: a quality related to inquisitive thinking such as exploration
Naches: proud pleasure, special joy.
Nginyiwarrarringu: a spasm of fright that causes someone to jump up and look about them.
Nostalgia: a sentimentality for the past, typically for a period or place with happy personal associations.
Oime: used to express grief or lamentation.
Overwhelmed: to be defeated completely.
Panic: anegativeemotion with a sudden sensation of fear.
Pique, a fit of: to arouse, stimulate, or excite.
Pity: a sympathetic sorrow evoked by the suffering of others.
Pronoia: having the sense that there is a conspiracy that exists.
Rage: a feeling of intense, violent, or growing anger.
Regret: a negative emotion to ones personal decision-making, a choice resulting in action or inaction.
Relief: a feeling of reassurance and relaxation following release from anxiety or distress.
Reluctance: unwillingness or disinclination to do something.
Can emotions be considered wrong or right?
No,emotionscannot be wrong.
They are experience, and you have little to no control over experiencing them when they occur.
Are emotion and cognition related?
Some psychologists believe that emotion cannot exist without cognition.
You have to be aware of what you are feeling for define it as being felt.
Refer tothisself-report, which captures 27 distinct categories of emotion bridged by continuous gradients.
Where Does Emotion Come From?
The thought of theemotion, or the emotion itself?
A common example used in psychology is this: You are walking alone at night.
You hear footsteps behind you.
You start to shake, your heart rate quickens, and your breathing slows.
While these physiological changes are occuring, you are also feeling fear.
So what came first?
The thought, or rather, the perception of danger?
Or does emotion exist in a vacuum, whether or not these other components are present?
This is still highly debated in Science.
What are your thoughts?